When you bring a fresh pc setup to your studio, the first technical thing that you should perform is the ‘disk partition’. Hard drives own terabytes of storage and maintaining that space is a must for any individual to carry out their day-to-day pc works.
And before doing that, a big question breaks out and it’s ‘what is the method for partitioning hard drives?’ Well, this tutorial will show you the two popular methods that gonna separate your HDD into 2-3 partitions.
But there is one thing that you should be aware of about partitioning disk drives and it’s about why there is a need for partitioning when you’ve one full space HDD attached under your pc/laptop.

Why Should I Partition My Hard Disk?
You don’t wanna throw all of your data into a single drive when you’ve other personal stuff to work on. Let’s say, your pc consists of a single system drive and you’re using it to store your projects, gaming data, personal files, etc.
And if somehow something gets corrupted in that system drive, you might have to perform a full format to restore your computer. And formatting will erase all your other personal data too including system files.
Well, that’s the main purpose to create a separate drive to play safe when there is a need to restore or format your system drive. There are also a few reasons behind partitioning hard drives like – running a separate os, to keep confidential data, for backing up data easily, etc.,
Methods Of Hard Disk Partition In Windows OS?
On opening Disk Management for partitioning hard drive, you may get a window to either choose MBR or GPT for partition. So let us know what these two are and which one you should prefer
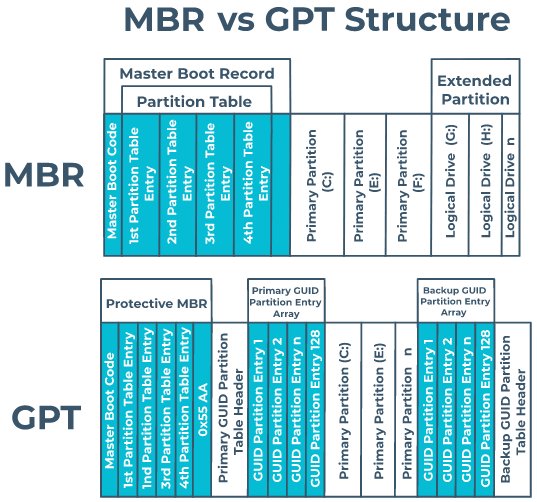
Method 1: Using MBR (Master Boot Record)
MBR first came out in 1983 which is known as the standard partition method for hard disks with space lower than 2TB.
Using MBR, you can create up to 4 primary partitions or 3 primary partitions plus one extended partition on this drive. Plus on the MBR disk, the partition size is stored in the length of 4 bytes (32 bit)
Method 2: Using GPT (GUID Partition Table)
GPT is used when the hard drive space is more than 2TB. When the GPT method is used, you can create up to 128 primary partitions of your HDD when compared to the MBR method. Plus on the GPT disk, the partition size is stored in the length of 8 bytes (64 bit).
In terms of Security, the major difference between MBR and GPT is that MBR stores the data in one place while GPT creates multiple copies across the drive. So you can figure out which is safer to go with, either take a risk to throw all of the data in one place or play safely by storing it at multiple places.
How To Perform Hard Drive Partition In Windows OS?
- Open Disk Management by Visiting Start or Win+R > “diskmgmt.msc” > OK.
- Right-click the partition on the disk and then choose Shrink Volume.
- Now input the space you want to change and click the Shrink button (Make sure you enter in Megabytes).
- Create Partitions on the unallocated space
- After shrinking the partition, you get unallocated space on this disk and you can create other partitions.
- Now Right-click the unallocated space and then choose New Simple Volume > Next.
- Enter the size of the volume you want to create and then select Next.
- Accept the default drive letter for the partition and move on to Next
- Choose the way to format the partition and press Next.
- Done!
Note : Take a full backup before diving into shrinking disk volumes.
You may also like-
- How To Verify Snapchat Without Phone Number
- Best 5 Apps To Recover Your Deleted Photos Or Videos
- How To See Twitch Chat While Streaming With One Monitor
- How To Know If Someone Blocked Or Removed You On Snapchat?
Final Words
It’s never the easiest task when you go through a disk partition or shrinking HDD volumes. There’s always some fear of losing data even if you have a good source of information about partitioning.
But if you would ever go through partitioning hard drives, the above two methods will work for you without any risk. Still, we prefer you to take a full backup of the drive before getting into partitioning volumes.


![How to Use ChatGPT Canva Plugin to Up Your Social Media Game [2025] How to Use ChatGPT Canva Plugin](https://techihd.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Use-ChatGPT-Canva-Plugin.jpg)
![How to Use One WhatsApp Account on Two Phones in [2025] One Whatsapp In Two Phone](https://techihd.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/two-whatsapp-in-one-phone-218x150.webp)
![How to Install an Intel or AMD CPU on Your Motherboard [2025] How To Instal Intel Or AMD CPU On Your Motherboard](https://techihd.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/WhatsApp-Image-2023-03-03-at-14.49.36.jpg)